Blockchain Basics & Cryptography
Blockchain Design Features
- Blockchain is a
timestamped append-only log. There is no editing or deletion. We can only add to an existing blockchain. - It is secured via cryptography
- Hash functions for tamper resistance and integrity
- Digital signatures for consent
Cryptographic Hash Function
- Convert any input into a unique fixed length output/a hash
- Deterministic: the same input always lead to the same output/hash
- Can be efficiently computed
- Preimage resistant: it’s infeasible to reverse engineer (not mathematically impossible)
- Collision resistant: it’s infeasible that two inputs will generae the same hash
- Avalenche effect: Changing the input slightly will completely change the has
- Puzzle friendliness: knowing the part of the input will not help much in finding the rest of the input
Block Header
Blockheader is a 80-bytes (160-bit) data containing six fields.
Bitcoin Blockheader of Block at Height 645,536

Bitcoin Blockheader Data Fields

Merkle Tree
A tree structure in which each leaf node is a hash of a block of data, and each non-leaf node is a hash of its children.
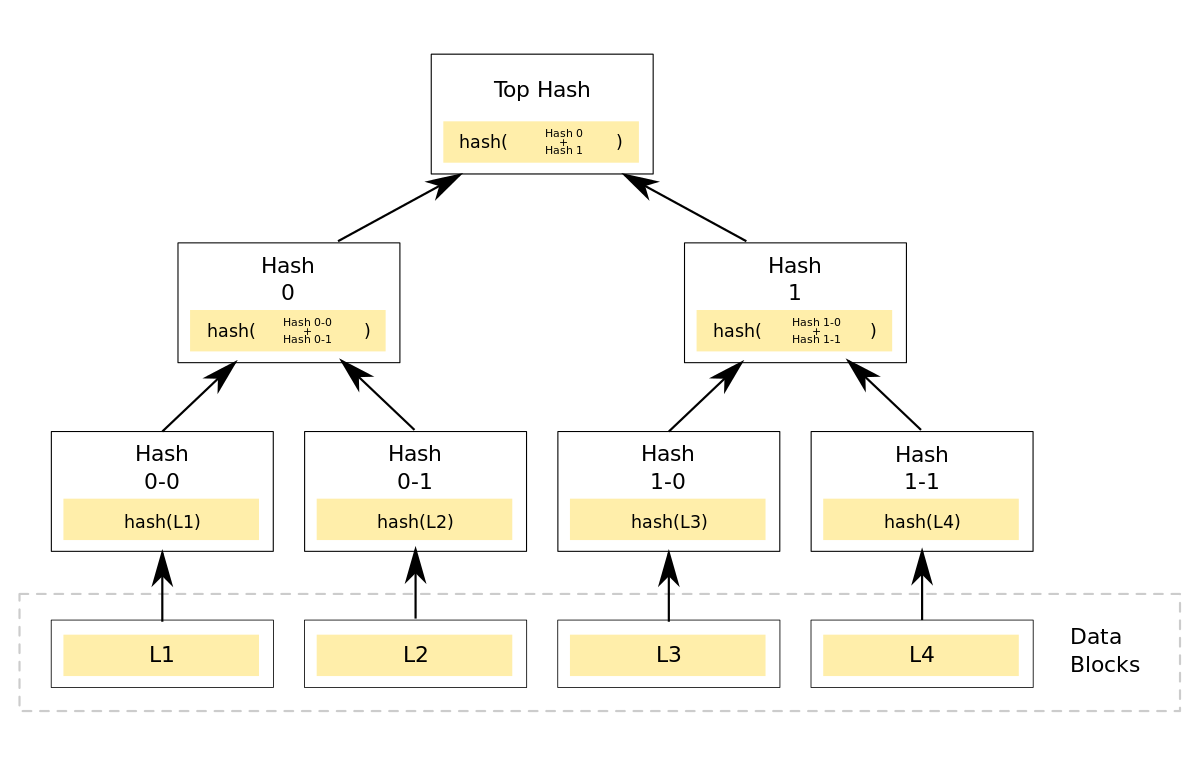 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merkle_tree
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merkle_tree
Asymmetric Cryptography & Digital Signatures
- A pair of public key and private key are generated from random numbers using one-way functions so it is imfeasible to deduce the private key from the public key
- The sender encrypts the message using the receiver’s public key and one-way functions so it is not feasible to infer the original message
- The receiver can then decrypt the message using his private key