DP-900: Data Fundamentals
- Azure SQL Family of Services
- SQL
- ACID
- Database Administrator Tools
- JSON
- Data Engineering Tools
- Batch Vs Stream Processing
- Normalized vs Denormalized data
- Star vs. Snowflake Schema
- Clustered vs Nonclustered Index
- Strongly vs Eventual Consistency
- Synchronous vs Asychronous Data Trasmission
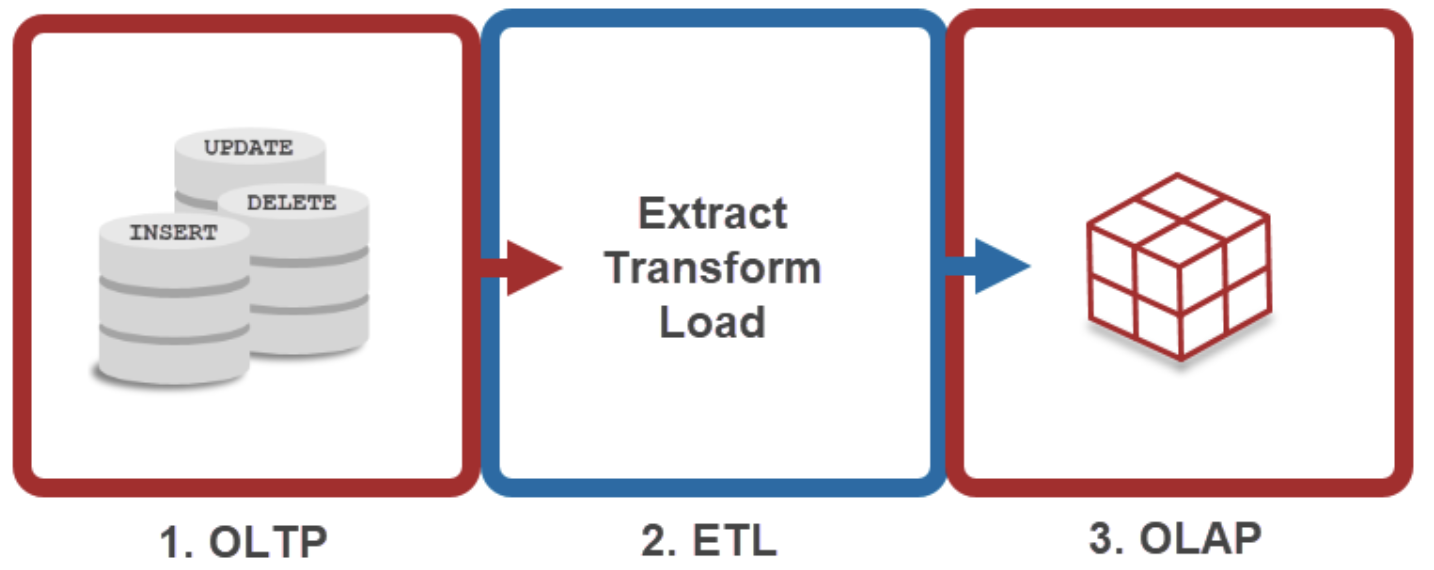
- OLAP vs OLTP
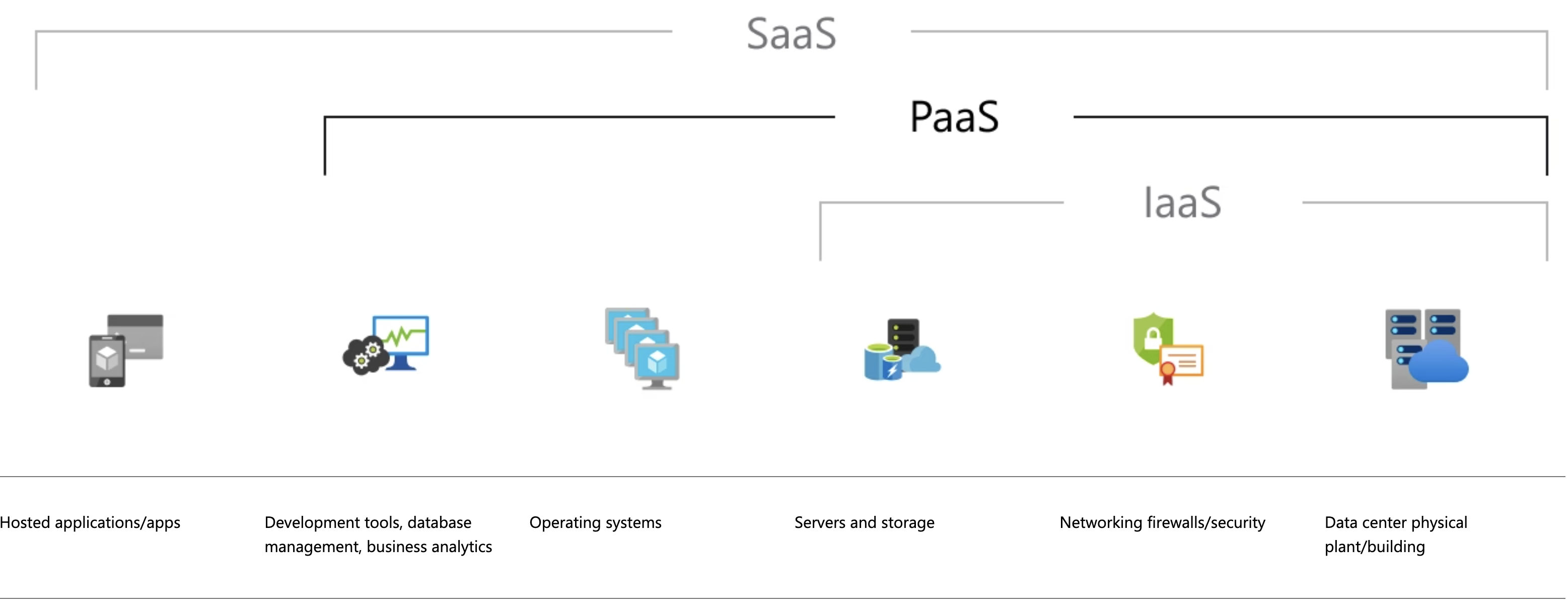
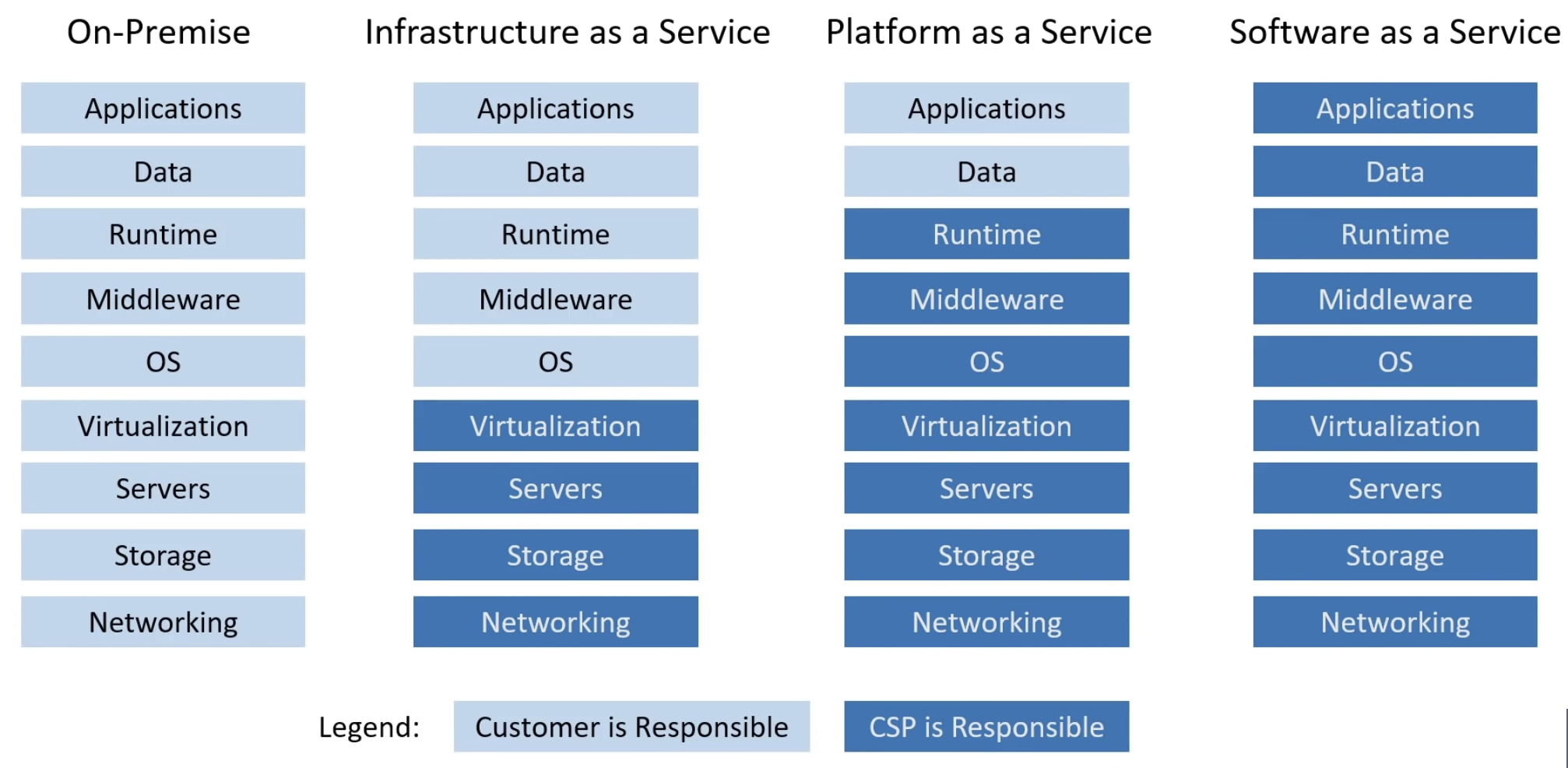
- SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS
- Data Storage
- Data Structure
- ELT vs ETL
- Data Analytics
- Azure Synapse Analytics
- Pipelines
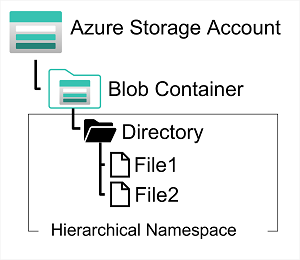
- Azure Storage Accounts
- Storage Tiers
- Mongo DB
- Cosmo DB
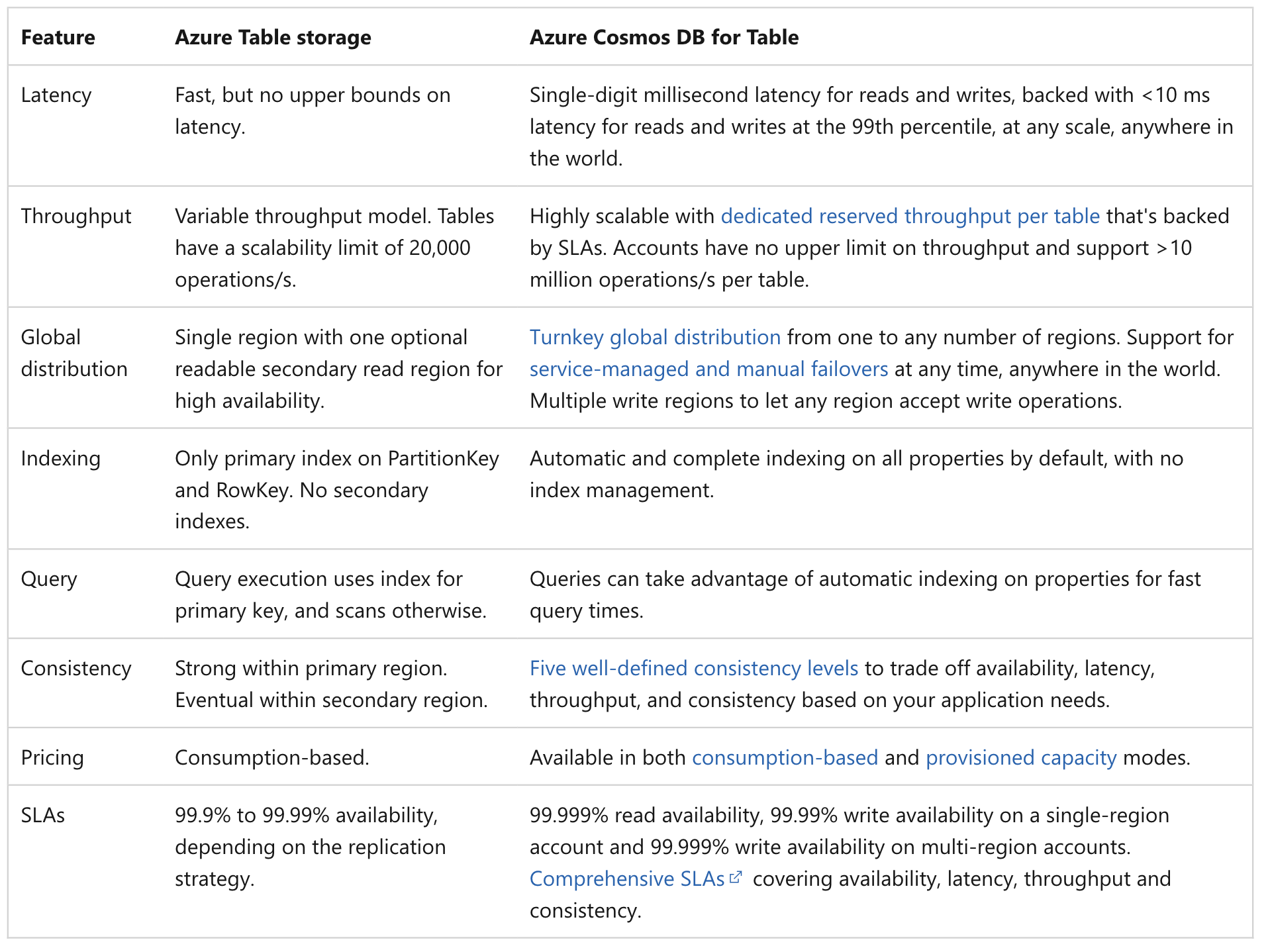
- Azure Tables vs. Cosmo DB for Tables
- Read Replica
- Connectivity Architecture
- Public vs Private Endpoint
- Role-Based-Access-Controls (RBAC)
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
- Dynamic Data Masking
- Private Links
- Apache Hadoop
- Apache Kafka
- Apache Spark
- Databricks
Azure SQL Family of Services
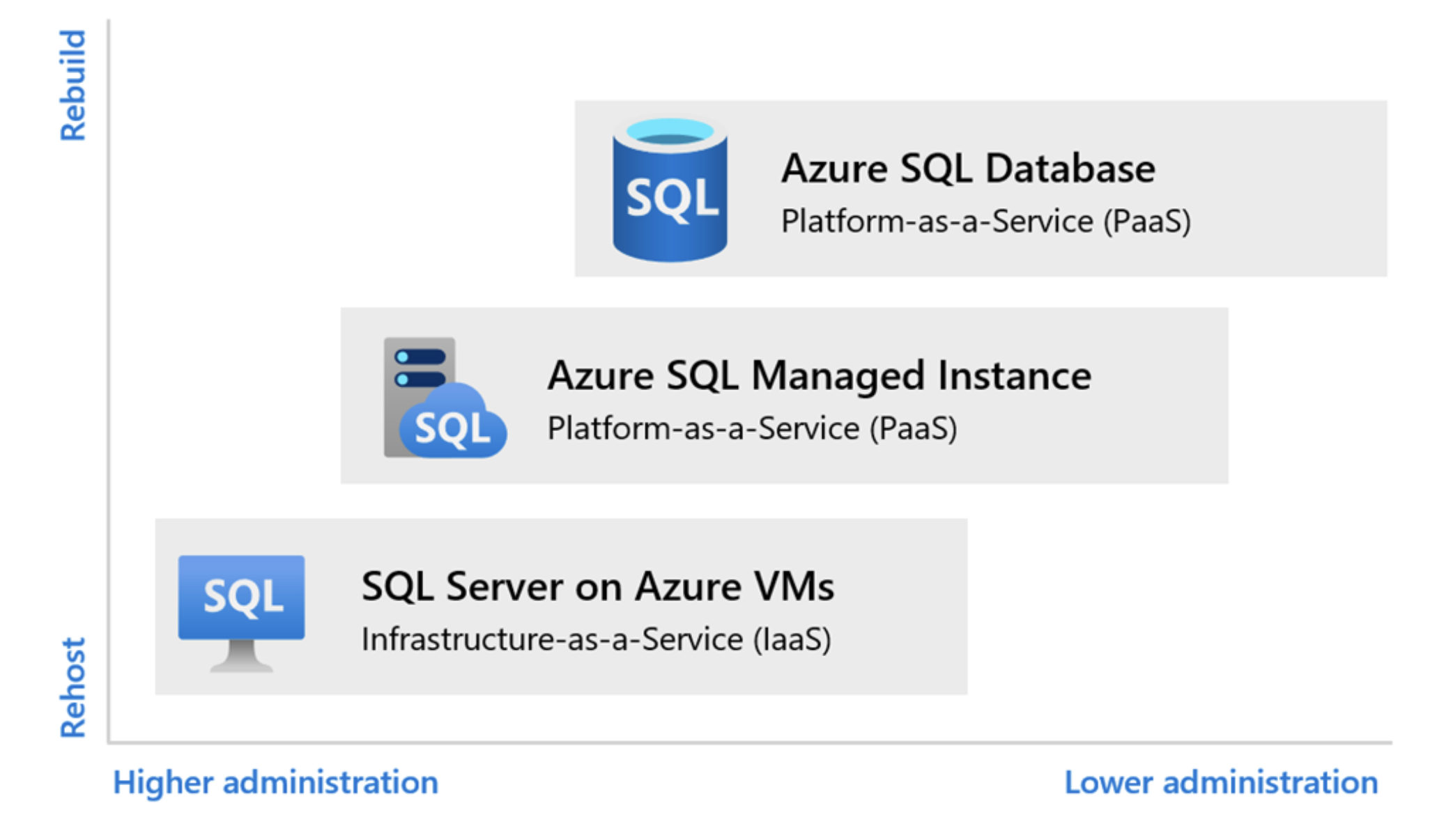
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/the-azure-sql-family-innovation-and-value-in-the-cloud/
SQL
Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL defines data structures. Use these statements to create, alter, or drop data structures in a database.
- ALTER
- Collations
- CREATE
- DROP
- DISABLE TRIGGER
- ENABLE TRIGGER
- RENAME
- UPDATE STATISTICS
- TRUNCATE TABLE
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DML affect the information stored in the database. Use these statements to insert, update, and change the rows in the database.
- BULK INSERT
- DELETE
- INSERT
- SELECT
- UPDATE
- MERGE
ACID
- Atomicity: each statement is treated as a single unit. Either the entire statement is executed, or none of it is executed.
- Consistency: ensures that transactions only make changes to tables in predefined, predictable ways.
- Isolation: when multiple users are reading and writing from the same table all at once, eachch request can occur as though they were occurring one by one, even though they’re actually occurring simultaneously.
- Durability: ensures that changes to your data made by successfully executed transactions will be saved, even in the event of system failure.
Database Administrator Tools
- Azure Data Studio
- Graphic interphase for managing on-premises and cloud-based data services
- Runs on Windows, Mac and Linux
- SQL Server Management Studio
- Runs on Windows
- More mature than Azure Data Studio
- Azure Portal and CLI
- Manage SQL database configurations
JSON
"Customer": {
"first_name" : "Sammy",
"last_name" : "Shark",
"location" : "Ocean",
"websites" : [
{
"description" : "work",
"URL" : "https://www.digitalocean.com/"
},
{
"desciption" : "tutorials",
"URL" : "https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials"
}
],
"social_media" :
{
"description" : "twitter",
"link" : "https://twitter.com/digitalocean"
}
}
Customeris a root objectWebsiteis a nested array, as indicated by the square bracket [ ]Social_Mediais a nested objectData Engineering Tools
- Azure Synapse Studio
- A central portal to manage Azure Synapse, Azure data factory (data ingestion) and Synapse assets (SQL/Spark pools)
- Knowledge SQL
- Create databases, tables, views, etc
- Azure CLI
- Support SQL command to connect to Microsoft Server
- HDInsights
- Streaming data or applying ELT jobs via HIVE, PIG, Apache Spark
- Azure dATABRICKS
- Streaming data or applying ELT jobs via Apache Spark
Batch Vs Stream Processing
- Batch Processing
- Not real time
- Ideal for large processing workloads
- Cost effective
- Stream Processing
- Offer real-time analytics
- More expensive
Normalized vs Denormalized data
- Normalized data
- Easier to maintain data integrity
- Little to no redundant data
- Optimized for data storage
- Querying is slower
- Increases throughput for writing
- Better suited for transactional database
- Denormalized data
- Harder to maintain data integrity
- Redundant data is common
- Storage is less optimal
- Querying is fast
- Increases throughput for reading
- Better suited for analytical database
Star vs. Snowflake Schema
| Star | Snowflake |
|---|---|
| Fact tables, dimension tables | Fact tables, dimension tables, sub-dimension tables |
| Top-down model | Bottom-up model |
| Has redundancy, more storage space | No redundancy, less storage space |
| Less JOINs, less complex queries | More JOINS, more complex queries |
| Shorter execution time | Longer execution time |
Clustered vs Nonclustered Index
- Clustered index
- Sort and store the data rows in the table based on their key values.
- There can be only one clustered index per table, because the data rows themselves can be stored in only one order.
- When there is no clustered index, data rows are stored in an unordered structure called a heap.
- Nonclustered index
- Strongly consistent
- Each query returns the most update to date (consistent) data
- At the cost of high latency
- Eventually consistent
- Query may return stale data at first
- Time taken to get consistent may or may not be defined.
- Low latency
Synchronous vs Asychronous Data Trasmission
- Synchronous
- Sender and receiver are permanently synchronized using a common timing signal
- Guarantee consistency of data at time of access
- Can only access data once transfer is complete
- e.g. chat app, streaming services
- Asychronous
- Sender and receiver are synchronized only during transmission, by a starting bit and a stop bit
- No guarantee of consistency
- Can access data anytime
- e.g. email
OLAP vs OLTP
- OLAP: Online Analytical Processing
- Multiple data sources
- Long and complex queries, with an emphasis on read (SELECT)
- Few transactions
- Throughput sensitive
- OLTP: Online Transaction Processing
- Single data source
- Short query, with an empahsis on write (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS
Data Storage
Data Warehouse
- A central repository of relational data designed for analytical purpose
- Can return queries very fast
Data Mart
- A subset of data warehouse, allowing teams or department to have control over their own datasets
- Generally read only
Data Lake
- A centralized repository that holds vast amount of raw data in structured, semi-structured, or unstructured form
- Mainly designed for machine learning and big data analysis
Data Lakehouse
- Compoared to a data warehouse:
- Support video, audio and text files
- Support data science and ML workloads
- Support both ELT and streaming
- Compared to a data lake:
- Perform BI tasks well
- Easier to set up and maintain
- More management features
Data Structure
Unstructured data
- A bunch of loose data
- MS products: Sharepoint, Azure Blob Storage, Azure files, Azure Data Lake
Semi-structured data
- Has some form of relationship
- XML: a markup lanaguage that looks similar to HTML
- JSON: a text file that is composed of dictionaries and arrays
- RCFiles: a storage format designed for MapReduce framework
- ORC: a columnar data structure that’s 75% more efficient than RCFiles; works well with HIVE
- AVRO: a row wise data structure for Hadoop system
- PARQUET: a columnar data-structure for Hadoop system
- MS products: Azure Tables, Azure CosmoDB, MongoDB, Apache Cassandra
Structured data
- Most common structure is tabular
- MS products: MySQL, Postgres, Azure SQL, Azure Synapse Analytics
ELT vs ETL
- Extract, Transform and Load
- Loads data first into a staging server and then to the target system
- Used for on-premise, relational and structured data
- Commonly used for small amount of data
- Doesn’t provide data lake suport
- Easy to implement
- Extract, Load and Transform
- Loads data directly into the target system
- Used for scalable structured and unstructured data
- Used for large amount of data
- Provide data lake support
- Require specialized skills to implement
Data Analytics
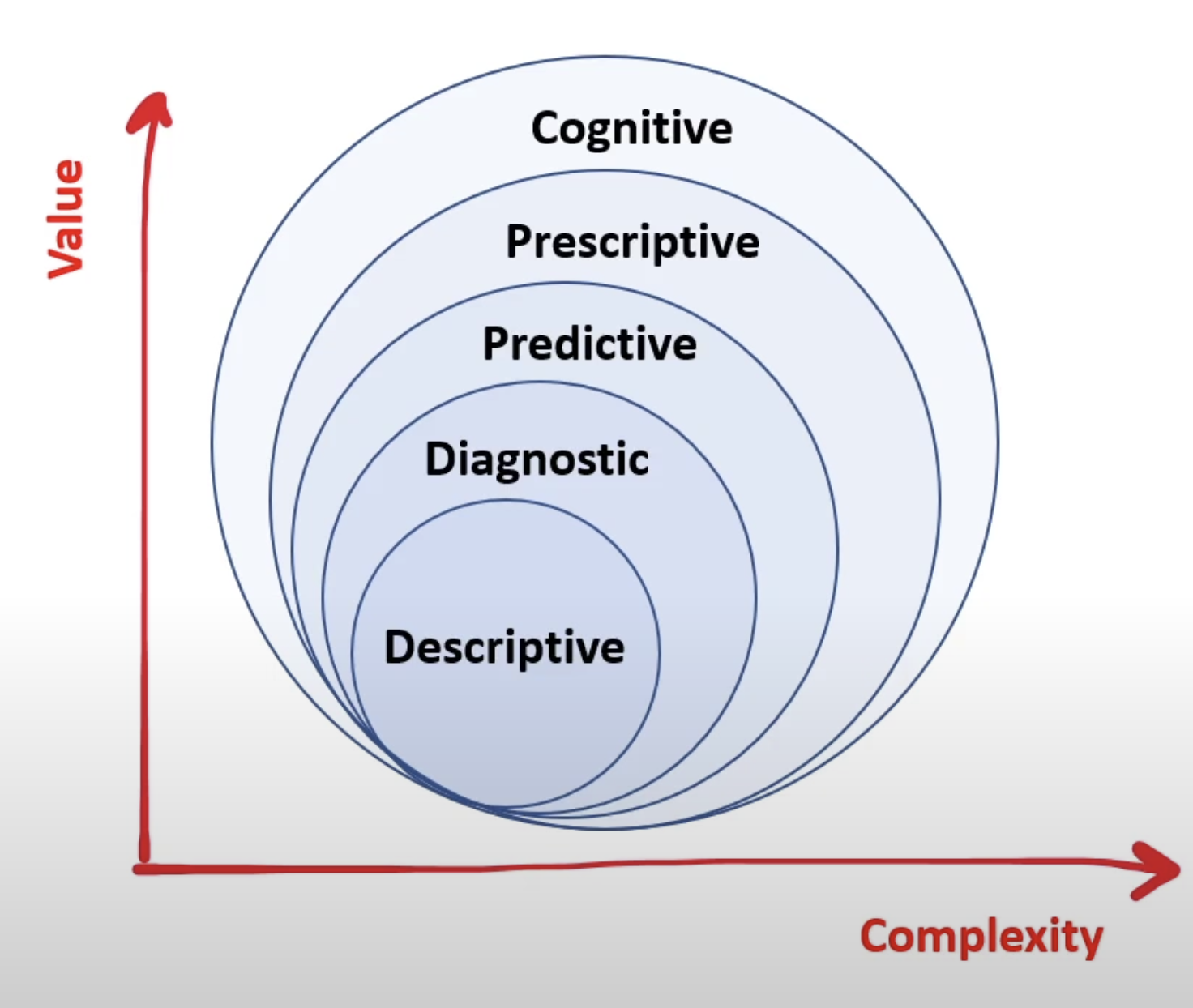
- Description analytics - what happened?
- Diagnostic analytics - why did it happen?
- Predictive analytics - what will happen?
- Prescriptive analytics - how can we make it happen?
- Cognitive analytics - what if this happens?
Azure Synapse Analytics
- A data warehouse and unified analytics platform
- Synapse SQL is a distributed version of T-SQL with built-in streaming capabilities to load data from cloud data sources
- Offer both serverless and didicated resource models
- Serverless: for unpredicable workloads
- Dedicated: for predictable workloads
- Can seamlessly integrate with Apache Spark
Pipelines
- A logical grouping of activities that together perform a task.
- Azure Data Factory and Azure Synapse Analytics have three groupings of activities
Storage Tiers
- Hot tier: An online tier optimized for storing data that is accessed or modified frequently; highest storage costs, but the lowest access costs.
- Cool tier: An online tier optimized for storing data that is infrequently accessed or modified. Data in the cool tier should be stored for a minimum of 30 days.
- Archive tier: An offline tier optimized for storing data that is rarely accessed, and that has flexible latency requirements, on the order of hours. Data in the archive tier should be stored for a minimum of 180 days.
Azure Blob
- Blob is a object-store that is optimized for storing massive amount of unstructured data, such as image files
- Azure Storage supports 3 types of blobs:
- Block blobs
- Store text and binary data
- Can be managed invidividually
- Store up to 4.75 TB of data
- Append blobs
- Optimized for append operations
- Ideal for scenarios such as logging data
- Page blobs
- Store random access files up to 8TB
- Store virtual hard drive files and serve as disks for Azure virtual machine
- Block blobs
Azure Files
- A fully managed file share in the cloud
- Can be mounted concurrently by cloud or on-premises deployments of Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Azure Tables
- Stores non-relational structured data - NoSQL key/value data - with a schemaless design
- Can be hosted on Account Storage - designed for a single region and single table
- Can be hosted on CosmosDB - designed for scale across multiple regions
Mongo DB
- An open-source database that stores JSON-like documents
- The primary data structure is called Binary JSON (BSON)
- Has more data-types than JSON
- Designed to be efficient both in storage space and scan speed
Cosmo DB
- Supports different kinds of NoSQL database engine through API
- Core SQL (document data)
- Azure table (key/value data)
- API for MangoDB (document data)
- API for Gremlin (graph data)
Azure Cosmos DB’s Gremlin API
Azure Tables vs. Cosmo DB for Tables
Read Replica
- A copy of the database that is kept sync with the original database
- Used to offload read requests or analytics traffic from the primary instance
Connectivity Architecture
- Proxy
- Connections are proxies through a gateway
- Increased latency and reduced throughput
- Intended for workloads from outside the Azure network
- Redirect
- Direct connection
- Reduced lantecy and improved throughput
- Intending for workloads from inside the Azure network
Public vs Private Endpoint
- Public: reachable outside the Azure Network over the Internet
- Private: only reachable within the Azure Network
-
Role-Based-Access-Controls (RBAC)
- SQL DB Contributor
- Manage SQL databases
- Cannot give access to others
- SQL Managed Instance Contribute
- Manage SQL Managed Instances and require network configuration
- Cannot give access to others
- SQL Server Contributor
- Manage SQL servers and databases
- Cannot give access to others
- SQL Security Manager
- Manage the security-related policies of SQL servers and databses
- Cannot give access to others
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
- Encrpyts data-at-rest
- Uses a database entryption key (DEK) which is a symmetric key (same key used for both encryption and decryption)
- Can be applied to
- SQL Server
- Azure SQL Database
- Azure Synapse Analytics
Dynamic Data Masking
- A central data masking policy acts directly on sensitive fields in the database.
- Designate privileged users or roles that do have access to the sensitive data.
Private Links
- Allows secure connections between Azure resources so traffic remains within the Azure network
Apache Hadoop
- An open source framework for distributed processing of large datasets
- Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS): a resilient and redundant file storage distributed on clusters of common hardware
- Hadoop MapReduce: writes apps that can process multi-terabyte data in parallel on large clusters of common hardware
- HBase: an open-source non-relational distributed database
- YARN: manages resources, nodes, containers and performs scheduling
- HIVE: generating reports using SQL
- PIG: a high level scripting language to write complex data transformations
Apache Kafka
- An open source streaming platform to create high-performance data pipelines, streaming analytics, data integration…
- Use JAVA
Apache Spark
- An open source unified analytics engine for big data and machine learning
- Run worloads much faster than Hadoop
Databricks
- Provides fully managed Apache Spark clusters